Tech
Chatbots are Predicted to Reduce Business Costs by 2022

Artificial Intelligence is taking businesses to another level. And chatbots is one kind of Artificial Intelligence that increases productivity and reduces costs. It was Oracle which predicted that 80% of businesses plan will be using chatbots by 2020. And it also predicted that chatbots are expected to reduce business costs by $8 billion by 2022.
Avi Benezra, who is the CTO of SnatchBot, said that chatbots really helped them cut the costs and it bumped up the conversion rates. That is why others are now adopting chatbots more rapidly.
AI technology is indeed changing every aspect of our lives. Now chatbots aren’t just about gadgets but there are also Chatbot lawyers, Chatbot therapists and more. Chatbots are also changing the business-to-consumer (B2C), business-to business (B2B) and business-to-employee (B2E).
For a single task a single bot is enough. The task takes place through a fixed set of scenarios in the single use bot. But when there are multiple tasks then multi-tasking bots come to play.
The Chatbot platform must provide the ability to track and streamline multiple functions simultaneously within a single task Chatbot. And it is important to have the ability to create and deploy a multi-purpose chatbot for communication.
For multiple tasks to be performed the chosen platform must offer pre-built bots. And these bots must be ready to deploy in order to address specific tasks. These tasks could consist of customer support, lead generation, and many more. Also the bots must be customizable. This feature makes it easy to further interactions according to the type of business you are dealing with.
The platform for the Chatbot development program must have customized user interfaces.There is a preferred channel for every Chatbot. And it could be various channels like websites, mobile apps, social media, email and SMS. Bots can also interact with Skype, Slack and Telegram, but it’s mostly for corporate purposes.
NLP and Speech Support are the most used tools of best chatbots platform in field of language and speech. These tools help them to train and to maintain the accurate interactions, and conversations through both text and speech. By the NLP and Speech Support chatbots understand the user and give relevant response.
Bots can perfect their natural language processing capabilities with the help of Machine learning. Therefore the chatbots must be smart and intelligent so that they will gauge and remember the data and learn from it. The interactions with customers will improve over time and they collect the information from the conversations. This way they can serve the customer’s request once they hone their machine learning and language.
An internal bridging map is vital for the Chatbot platform. It helps with the sharing of messages between users. Moreover, chatbots and the cross-functional systems should also have the bridging. A bridge records the success and the failures. It categorizes messages, so that the bot manager can have a comprehensive understanding of the chatbots function.
Chatbots are indeed the future of business, as they will help cut the costs. But proper research is necessary to build a right bot platform. The features must match the functionality of the chatbot used in a particular business.
Tech
CypherFace Targets Payment Fraud with Pre-Transaction Biometric Verification
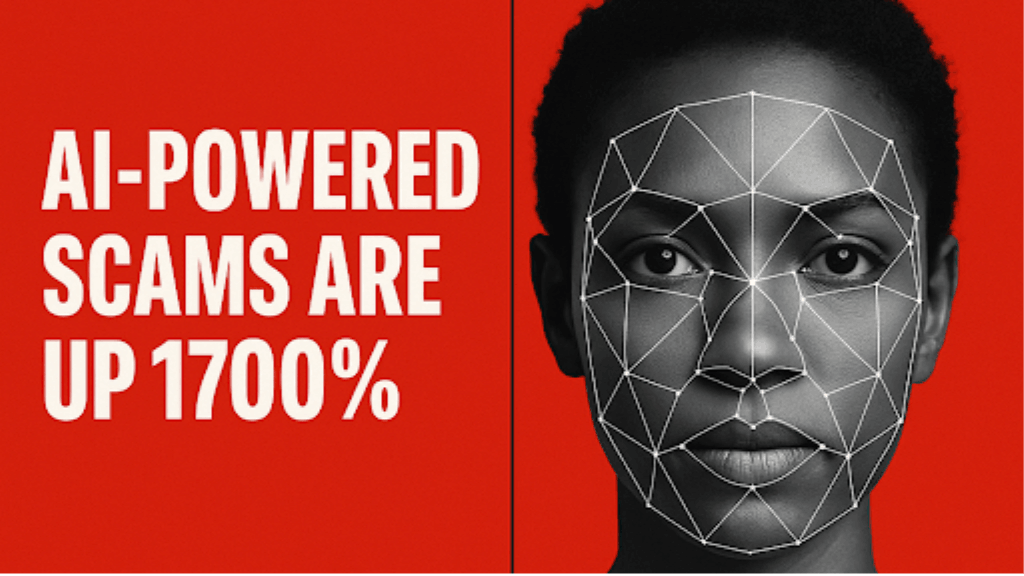
A U.S.-based fintech company has deployed a facial biometric system that verifies user identity before digital payments are processed. CypherFace, which began commercial operations in 2024, is positioning its technology as a proactive defense against payment fraud that now costs billions annually.
Founder Syed Samir Hassan said the company developed the platform in response to the limitations of fraud detection systems that identify problems after transactions have already occurred. “Traditional fraud tools are reactive by design. They analyze patterns and flag suspicious activity, but the money has often already moved. We’re stopping it before the transaction completes,” Hassan said.
The Fraud Problem
Digital payment fraud has grown substantially despite existing security measures. Payment fraud in the European Economic Area increased to €4.2 billion in 2024, up 17% from 2023, according to data from the European Central Bank and European Banking Authority. Credit transfer fraud alone saw a 24% increase.
Synthetic identity fraud, which involves creating fictitious identities using combinations of real and fabricated personal information, has become particularly problematic. False identity cases increased 60% in 2024 compared to the previous year. These synthetic identities often pass initial verification checks because they use legitimate data elements.
Hassan said CypherFace was designed specifically to address this threat vector. “Synthetic identities work because they look clean on paper. They pass KYC checks. They build credit histories. But they can’t pass a live biometric verification tied to a real person. That’s the fundamental flaw we exploit.“
The company reports that fraudsters increasingly use AI-generated documents and deepfake technology to bypass security systems. CypherFace’s liveness detection technology is designed to identify these sophisticated spoofing attempts during the authentication process.
How the Technology Works
CypherFace provides businesses with an API that integrates into payment infrastructure. When a user initiates a transaction, the system prompts for facial verification. The technology captures and encrypts a facial scan, then applies AI-driven liveness detection to confirm a physically present individual is authorizing the payment.
The system processes the verification in real time without storing raw biometric data. Facial scans are converted into encrypted, non-reversible hashes. The platform returns only a verification result to the merchant, indicating whether the transaction should proceed.
“We designed this to be invisible to legitimate users and impossible for fraudsters,” Hassan said. “A real customer takes two seconds to verify. A criminal using a stolen card or synthetic identity can’t get past the liveness check. The math is simple.“
Deployment and Results
An e-commerce payment processor deployed CypherFace across its checkout infrastructure in late 2024. The processor was experiencing elevated chargeback rates driven by card-not-present fraud. Within 45 days of implementation, CypherFace flagged more than 1,200 fraudulent transactions that had previously bypassed existing security layers.
The integration reduced chargebacks by 62% in the monitored segment. The processor reported improved merchant satisfaction as legitimate transactions experienced minimal additional friction. The company has since expanded CypherFace to additional merchant accounts.
Hassan noted that the technology addresses a specific gap in payment security. “Most fraud prevention happens at the network level or through transaction monitoring. We’re adding a layer that asks a simple question: is the person trying to make this payment actually who they claim to be? If they’re not, the payment doesn’t happen.“
Market Expansion
CypherFace currently operates in the United States and is preparing to expand into Canada and Mexico in 2026. The company is targeting payment processors, merchant acquirers, and platforms with high transaction volumes and elevated fraud exposure.
Hassan said the company sees demand from businesses struggling with the cost of chargebacks and fraud losses. “Every fraudulent transaction costs more than the transaction value when you factor in chargeback fees, lost merchandise, and reputational damage. Businesses are looking for solutions that actually prevent fraud rather than just detect it after the fact.“
The fintech sector has broadly adopted biometric authentication, with major banks and digital financial platforms using facial recognition and fingerprint scanning for account access and transaction authorization. CypherFace is focusing specifically on payment verification rather than account login.
“We’re not trying to replace existing security. We’re adding a verification layer at the most critical point in the transaction flow,” Hassan said. “When money is about to move, we make sure the right person is authorizing it. Everything else is secondary to that.“
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle7 years ago
Lifestyle7 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health7 years ago
Health7 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
