Health
Sclerotherapy: An Effective Treatment for Eliminating Spider Veins
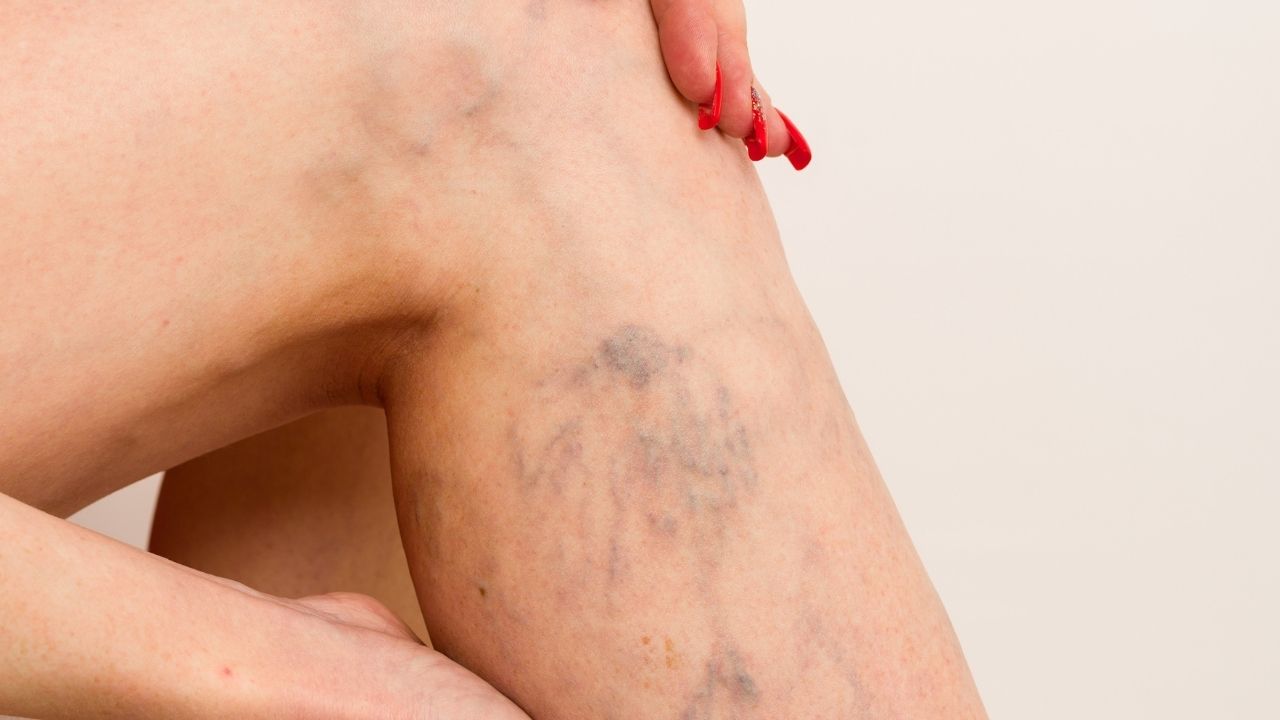
When the temperatures are hot, some flaws may come to light. You may be unable to wear your carefree shorts, swimwear, or short skirts in spring or summer due to spider veins. Although these are conspicuously visible, doctors can use sclerotherapy in Glen Rock to eliminate spider veins. You can benefit from a relatively safe procedure that not only improves your appearance but prevents other complications.
Boosts the appearance of your legs
Attractiveness is a major concern for most people, and this includes beautiful legs. Spider veins appear as reddish-blue vessels on the lower legs and thighs. They may dent your self-confidence and, therefore, sclerotherapy becomes an option.
Benefit from modern technology
With modern technology, your doctor can remove spider veins through a painless and minimally visible procedure. It takes less time and you can resume your normal activities immediately after the session. The doctors use a thin needle to inject a sclerosing agent into the spider vein.
The vessel wall disintegrates and sticks to the opposite side such that the vessel can no longer get blood supply. Although it is a painless process, your doctor may apply local anesthesia to numb the treatment area.
How does sclerotherapy differ from laser vein treatment?
Laser treatment is non-invasive and involves directing a beam of light into the affected veins, thereby destroying them. It uses laser energy to target the specific veins by warming the vessel while protecting the surrounding areas from heat.
Unlike laser technology that uses heat, sclerotherapy is a safer option for treating spider veins buried deeply under the skin. These veins may differ in terms of pressure and size, and laser beams often fail to penetrate deeper into the underlying tissues. Thus, some veins remain, and there is also a risk of heart damage resulting in redness, scars, and swelling. Besides, sclerotherapy does not require cooling the skin to prepare it for laser treatment.
What causes spider veins?
Think of your venous system as a tree with branches. Spider veins are tiny branches or veins of the vascular system that run under the skin. Excess weight, pregnancy, and weak connective are the primary causes of spider veins. Also, sitting or standing for long hours, lack of exercise, and alcohol can promote their occurrence.
Similarly, wearing high heels can speed up the development of spider veins by causing blood to build up and cause pressure on your vessel walls. Eventually, they expand and can be seen from the outside.
How long does the treatment take?
The treatment can last up to six weeks, after which the vein disappears into the body and blood reroutes into healthy veins. Your doctor personalizes your treatment program depending on the complexity of the veins.
Your doctor assesses your suitability for the treatment and pregnant women are excluded from the procedure. If you are on supplements, have a history of blood clots or are above 75 years, this procedure does not apply to you.
You can benefit from the proper treatment depending on your specific goals. Speak to a vein specialist at New Jersey Sports and Pain Medicine for consultation.
Health
BioLongevity Labs: How Two Biohackers Are Making Longevity Safe for the Mainstream

Humans have been looking for ways to extend their lifespan for hundreds of years. Medicine has made impressive strides, but for many, the effects of aging are still painfully real.
Through BioLongevity Labs, biohackers and entrepreneurs Jay Campbell and Josh Felber aim to introduce ordinary people to potentially life-changing compounds called peptides. Campbell and Felber come from very different backgrounds.
Campbell is a five-time international bestselling author and globally recognized leader in the health-optimization space. Felber is a serial entrepreneur who excels at scaling businesses.
For both men, BioLongevity Labs is more than just a business venture — it’s about helping everyday people discover something that just might prolong and improve their lives.
“Your body inevitably changes as the years pile on,” says Campbell. “Your energy drops, and wrinkles start showing up uninvited. Peptides can change everything.”
Many people have probably heard the term “peptide” in passing. Some may know they’re associated with longevity. Most people just don’t have a strong grasp of how they work.
A peptide is a short chain of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. Essentially, peptides are like shorter, simpler proteins. That might sound unremarkable, but the real magic of peptides lies in how they work.
They function as signaling or “messenger” molecules telling the body to perform specific functions. Many peptides function similarly to hormones. A relevant example is GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists. This class of medications includes semaglutide and tirzepatide, two wildly popular weight-loss drugs.
“These peptides aren’t just another biohacking fad,” Campbell explains. “They enhance insulin secretion and suppress glucagon release to balance blood sugar levels and promote sustainable weight loss”. But what sets GLP-1 receptor agonists apart is their ability to regulate hunger.
Through the reduction of appetite and increased feelings of fullness, it is far easier for dieters to stick to a calorie deficit.” Although GLP-1 receptor agonists are widely prescribed, most peptides aren’t.
Campbell asserts, because many peptides have the potential to cure illnesses by treating the fundamental root cause, they go against America’s “sick care” model of healthcare. They potentially threaten drug companies and their bottom line.
“Peptides are simultaneously a dream come true for mankind and the worst possible nightmare for the pharmaceutical industry,” says Campbell. “It’s not a conspiracy theory. It’s pure economics and psychology in action. People will do whatever it takes to make as much money as possible in a free-market society, even if it means suppressing a superior solution.”
Patients probably aren’t going to be introduced to peptides through the healthcare system. Many discover them on their own. But for the many people who don’t have a solid understanding of how they work molecularly or even what dose to take, there is a risk. That’s precisely what BioLongevity Labs’ co-founders are attempting to address.
Jay Campbell has dedicated his life to educating people about therapeutic peptides and optimized hormones, and along with his partner Josh Felber, they’ve created a company offering filler-free, third-party tested peptides and bioregulators.
Campbell and Felber stress the fact that BioLongevity Labs isn’t meant to be a replacement for traditional medical care. Instead, its products bridge the gap between clinical and extra-clinical care. There’s no magic pill or single solution to solve the problem of aging.
But thanks to the development of specialized peptides, bioregulators, and small molecules, we’re closer than we’ve ever been before.
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle7 years ago
Lifestyle7 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health7 years ago
Health7 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
