Lifestyle
Charles Winn gives the Lowdown on the World’s ‘Fine Wine’ Capital
The majority of the world might remain in lockdown amid the ongoing coronavirus pandemic, but for some industries life must continue as normal, such as for ‘fine wine’. Whilst the rest of the world locks down, in Bordeaux – the fine wine capital of the world – producers are hard at work preparing their crops for the next season.
Geography
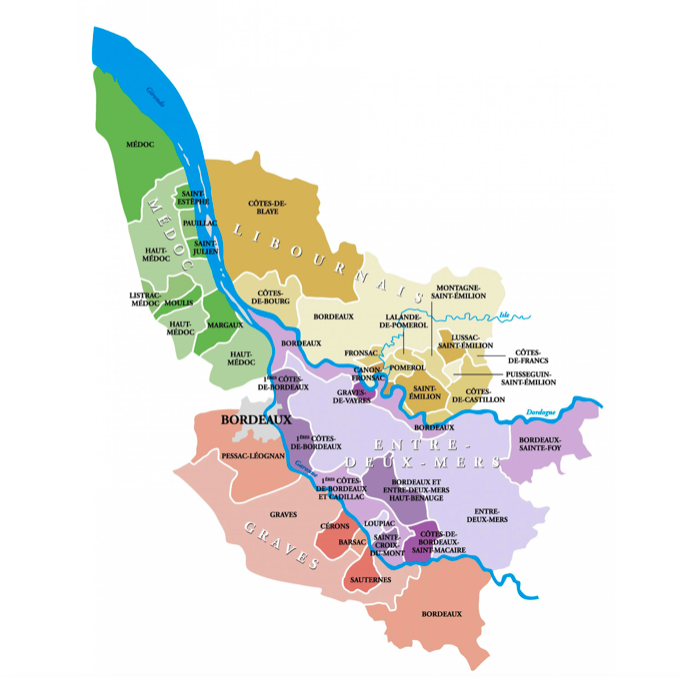
A port city on the Garonne River in southwestern France, Bordeaux is renowned globally for its famous wine-growing regions. A river runs directly through the region, and on the West side sits Gironde and Garonne. Typically, these regions are known for wines such as Sauvignon. On the East side of the river nestles Dordogne, known primarily for Merlot.
In total, Bordeaux has 57 grape-growing regions making it the biggest wine producer in France. Originally made famous for its popularity with kings, nowadays, Bordeaux and its chateaus are popular tourist attractions.
The Wines
As one of the biggest wine-makers in the world, you might expect Bordeaux to produce a diverse range of different type of wines. However, more than 90% of the wine produced here is actually red, with the region specifically producing Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Merlot, Petit Verdot, Malbec and Carménère.
Having said this, in 2019 Bordeaux’s regulatory body approved four additional dark grape varieties to add to the list: Marselan, Touriga Nacional, Castets, and Arinarnoa.
Bordeaux’s First Growth wines (the term for a wine made specifically made in Bordeaux) are made by blending 70% Cabernet Sauvignon, 15% Cabernet Franc and 15% Merlot. In contrast, the White Bordeaux is made from Sémillon, Sauvignon Blanc and Muscadelle.

The History
Bordeaux’s wine-making history stretches back over many centuries. In 1855, the Association of Bordeaux Wine Merchants established official classification and certification of the wines after Emperor Napoleon III requested that they do so.
Ranking the wines from First Growths to Fifth Growths, the merchants evaluated market prices based on an evaluation of the previous years. They noticed that red wines which made the list came from the Médoc region, except for one: Château Haut-Brion from Graves.
Since this original classification in 1855, there have only been two changes. In 1856, Château Cantemerle was added as a Fifth Growth and in 1973, Château Mouton Rothschild was promoted from Second Growth to the elite First Growth classification. The latter change is a wine much loved and highly ranked by Charles Winn and its customers.

Château Margaux
Global flavour
It didn’t take long for the popularity of Bordeaux wine to grow all over the world. After King Henry II’s marriage to Eleanor of Aquitaine in 1152, an interest in wine from the Bordeaux region was prompted in England.
The marriage established the province of Aquitaine within France and England, and a new dark rosé wine was created, called ‘Claret’. This wine soon became the most common wine to be exported to Britain.
After the battle of Castillion in 1453, the Aquitaine region returned to the French. Since then, the word ‘Claret’ became anglicised and is still widely used today, due to the global popularity of the wine.
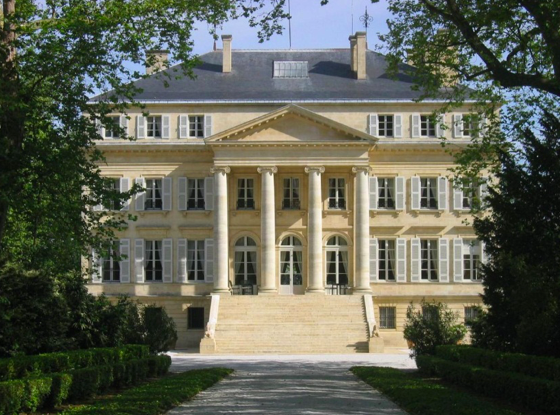

The exterior of the château
Lifestyle
When the Body Speaks: How Maryna Bilousova Helps Clients Heal Beyond the Physical

Our bodies hold onto what our minds try to forget until they speak up through tension, fatigue, or illness. It’s easy to overlook signs like tight shoulders, restlessness, or headaches. But often, these signals are connected to something deeper. Maryna Bilousova has built her work around helping people listen to what their bodies are really saying.
Like many of her clients, Maryna spent years in a high-stress environment, constantly pushing through. She knew how to perform, meet goals, and keep everything running. But peace was missing. Her body carried the weight of unspoken stress. That realization changed not only her life, it shaped how she supports others today as a transformation coach and subconscious pattern specialist.
Instead of focusing only on what’s visible, Maryna helps people look inward. She works with individuals who feel stuck in cycles they can’t explain, like burnout that does not go away or stress that feels out of proportion. Often, the root is not just a busy schedule. It’s emotional tension that’s been buried and ignored.
Looking Deeper Than Symptoms
Many people come to Maryna after trying traditional methods. They have done meditation apps, therapy sessions, or self-help routines. Still, something feels off. That’s where her work begins, not with fixing, but with listening.
She helps clients connect the dots between their physical symptoms and unresolved emotions. It’s not always about big trauma. Sometimes, it’s small moments that were never processed, guilt, grief, frustration, or shame. Over time, those emotions settle in the body.
Maryna recalls one client, a long-term cancer survivor, who returned years later with ovarian cysts. The physical fear was real, but so was the emotional weight she had been carrying from a past relationship full of betrayal and silence. Through their sessions, they uncovered and released that emotional residue. Weeks later, the cysts were gone. It was a reminder of how deeply the body can reflect our inner state.
Patterns That Keep Us Stuck
Maryna’s approach is not about chasing positivity or trying to fix everything at once. She focuses on patterns, how people speak to themselves, how they respond to stress, how they make decisions. Often, what feels like self-sabotage is actually an old belief playing out.
For example, someone who always avoids conflict might be carrying a belief that their needs don’t matter. Another who keeps overworking may feel that slowing down means they are falling behind. These beliefs often form early and show up in adulthood in ways that quietly run our lives.
Rather than offering surface-level solutions, Maryna holds space for clients to explore what’s really behind their choices. Her calm presence allows people to soften, reflect, and begin making changes that come from clarity, not pressure.
A Path Back to Yourself
The people Maryna works with are not looking for a quick fix. They want to feel lighter, clearer, and more like themselves again. Her clients often say that what changes is not just their mindset, it’s how they feel in their own skin. They start resting without guilt, setting boundaries without apology, and making choices that actually feel good.
Maryna believes that healing is not about doing more. It’s about slowing down enough to notice what your body and mind have been trying to say all along. When people start listening, they stop feeling like they have to fight themselves, and that’s when real change happens.
In a world that pushes us to ignore discomfort and keep going, Maryna offers something different: a place to pause, reflect, and reconnect. Because sometimes, healing does not start with doing, it starts with listening.
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle7 years ago
Lifestyle7 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle6 years ago
Lifestyle6 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health7 years ago
Health7 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
