Tech
Health Information Technology is the digitalized face of Healthcare Industry

Health Information Technology is a relatively new field in the healthcare. It is not entirely exclusive of the healthcare field. But they both exist in a beneficial symbiosis. Health IT is basically the area involving design, development, creation and use of Information systems for Healthcare Industry.
These systems may be interoperable or automated but they improve the medical care and public health. And they also help to lower costs and increase efficiency in the system by reducing errors. The IT sector does a remarkable job in the interplaying of Modern Health technology and Government policies regarding it. And companies like Global Data Systems are the faces behind managing the healthcare IT efficiently.
There are many forms of Health Information technologies. One of them is an EMR- Electronic medical record. It is a digital health record of a person which can be shared between multiple healthcare providers and agencies.
Like the EMR there is PHR and HIE, which are also digital records. PHR, is a personal health record of a patient an HIE is an exchange of records between various organisations. In HIE they can share various data through the systems.
PACS and VNAs are other picture archiving and communication systems. These interfaces help the healthcare professionals to store and manage patient’s medical images. And it is mostly the radiology department that uses this interface.
Patient Portals are also an efficient way of patients to handle their communication with the healthcare industry. Earlier Patients Portal was a clunky site. But the upgraded version helps patients communicate with their physician, pay the bills and check the reports too. And portals also have telemedicine systems that facilitate video conversations between patients and providers.
Government funds tons of money for the EHR system. Since the inception of Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical health(HITECH) Act in 2009, government funds hospitals for this program. The MACRA passed back in 2015( Medicare Access) and CHIP (Children’s health insurance program), all of this laws ensure government invests in the Health IT sector.
Even though the government funds the healthcare organisations it still faces challenges. There are some vendors who refuse to share the data, and some who stymie it. That is a concern for the federal officialS. But other than that there are many benefits of Health IT.
Tech
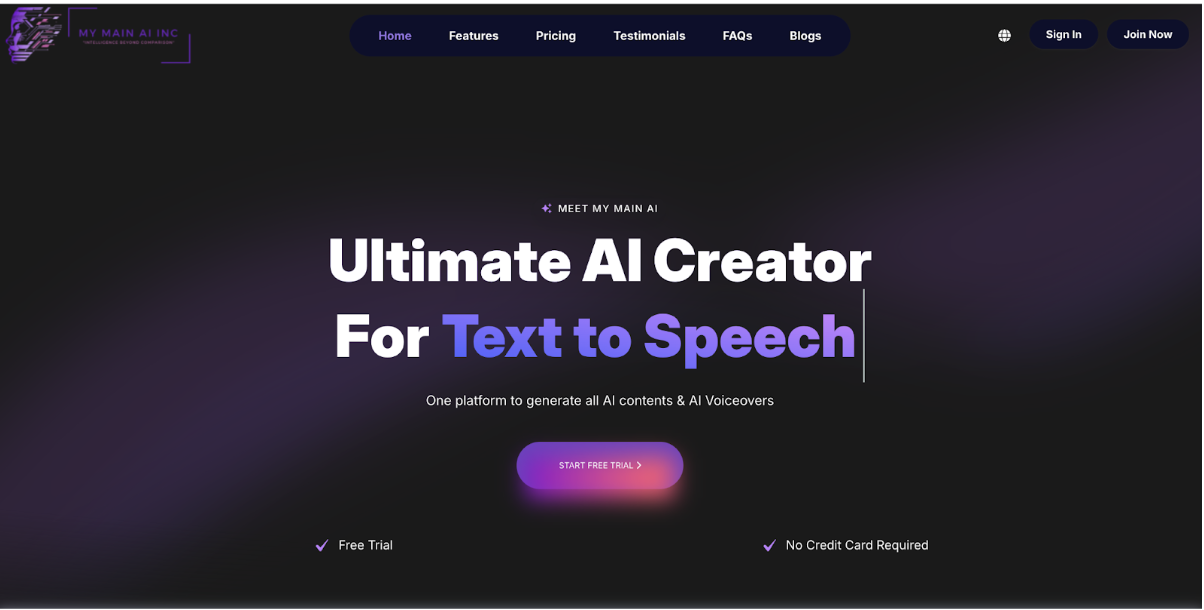
My Main AI Turns Complex Workflows into Simple, Voice-Driven Conversations
By: Chelsie Carvajal
Managing modern workflows often means juggling dashboards, documents, and long email threads before a single task is complete. My Main AI Inc, an AI technology platform that spans text, image, voice, and video, has built a system where many of those steps can be handled through spoken or written prompts instead of manual clicks.
Turning Tasks Into Conversations
My Main AI groups several automation tools around a voice and chat layer so users can move through work by giving instructions rather than configuring each step. The platform lists AI Web Chat, AI Realtime Voice Chat, AI Speech‑to‑Text Pro, and AI Text‑to‑Speech engines from providers such as Lemonfox, Speechify, and IBM Watson, creating a loop between spoken input and generated output.
Speech‑to‑text tools support accurate transcription of audio content in multiple languages, with options to translate those recordings into English. That capability gives businesses a way to record meetings, calls, or field conversations, then convert the results into text that can be summarized, edited, and turned into documents or scripts. Text‑to‑speech tools, including multi‑voice synthesis with up to 20 voices and SSML controls, take written content in the other direction, producing voiceovers for training, marketing, and support material.
Chat assistants extend the same pattern to files and websites. My Main AI lists AI Chat PDF, AI Chat CSV, and AI Web Chat, which allow users to ask questions of documents or site content through natural language prompts. Instead of sorting through long reports, a user can query a file, receive concise answers, and then send follow‑up requests to generate emails, briefs, or summaries in the same environment.
From Content Pipelines to Voice‑Led Workflows
The company reports that its platform connects to more than 100 models from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, xAI, Amazon Bedrock and Nova, Perplexity, DeepSeek, Flux, Nano Banana, Google Veo, and Stable Diffusion 3.5 Flash. Public materials state that these models support text, image, voice, and video generation in more than 53 languages, giving the voice‑driven tools reach across several regions and markets.
Content creation sits at the center of many of these workflows. My Main AI offers modules for blog posts, email campaigns, ad copy, social captions, video scripts, and structured frameworks such as AIDA, PAS, BAB, and PPPP. A user can dictate key points or paste a brief into the chat, receive draft text, ask the assistant to adjust tone or length, and then pass the result into voice synthesis to create a narrated version.
Visual tools fit into the same flow. DALL·E 3 HD, Stable Image Ultra, and an AI Photo Studio support image creation, product mock‑ups, background changes, and multiple variations from a single upload. AI Image to Video and text‑to‑video connections with engines such as Sora and Google Veo, alongside an AI Avatar feature labeled “coming soon,” make it possible to turn a spoken or typed brief into images, then into short clips that accompany the newly generated audio.
Why Businesses See Conversation as Infrastructure
Company data shared with partners cites more than 77,000 customers worldwide, annual revenue near 3 million dollars, and monthly revenue growth around 250,000 dollars, driven largely by subscription sales. The 49‑dollar plan is described as the best‑selling tier, with My Main AI presenting it as the entry point to the broader suite of conversational and automation tools.
Business‑oriented features show how these voice‑driven workflows connect to operations. The platform lists payment gateways such as AWDpay and Coinremitter, integrations with Stripe, Xero, HubSpot, and Mailchimp, and tools for SEO, finance analytics, dynamic pricing, wallet systems, and referrals. A manager can ask a chat assistant to pull figures, draft a report, and prepare customer messages, then move directly into sending campaigns or reviewing payments through linked services.
Company communications describe ongoing work on proprietary models, expanded training flows from text, PDFs, and URLs, and deeper tools for chat, analytics, and video. That roadmap suggests that My Main AI views conversation—spoken or typed—as a central control surface for complex workflows, with automation stepping in behind the scenes so users can focus on clear instructions rather than manual configuration.
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle7 years ago
Lifestyle7 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health7 years ago
Health7 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
