Blog
Pedestrian Accidents due to Negligence
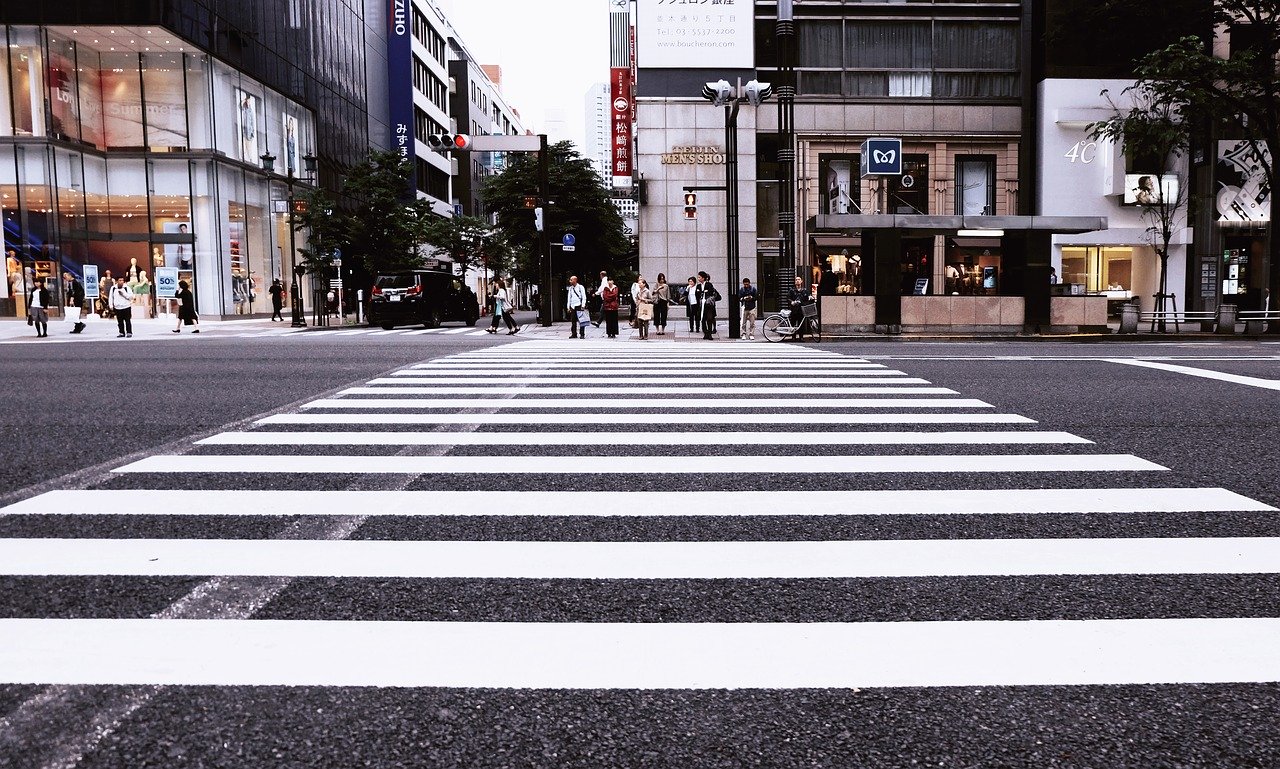

Pedestrian accidents usually result from motorists being at fault where they do not notice a pedestrian on the road. These accidents can also result from traffic violations, talking on the phone while driving or being preoccupied with any task while driving.
Who is at Fault?
Frustratingly, it can be difficult to determine who is at fault in a pedestrian accident. Walkers and joggers are responsible for staying on the sidewalk whenever possible, and it is important to wear bright, reflective clothing, to make yourself more visible to drivers. Also, if you must cross the road, wait until a stop sign, stoplight, or designated crosswalk to do so. If you are struck while jaywalking and you are wearing dark clothing, you may be less likely to receive financial compensation for any injuries you sustain.
Sadly, though, many times an accident is not a pedestrian’s fault. In many cases, accidents are primarily the result of unsafe driving. Some car and driver cause of pedestrian accidents include:
- Distracted or inattentive driving
- Driving too fast or recklessly
- Driving while intoxicated or under the influence of drugs
- Auto defects that can send a car out-of-control
- Failure to stop at stop signs and stop lights
- Ignoring pedestrian crosswalks
In a crash between a car and a pedestrian, there is no question as to who will suffer more serious accident injuries. Thus, it is also key for municipalities and road construction crews to build safe roads and sidewalks that are designed to protect pedestrians. Without sidewalks, pedestrians are placed directly in harm’s way and must share the road with drivers. Also, road construction companies should paint reflective white crossing stripes at crosswalks so that walkers and joggers have an obvious place to cross. Stoplights should have crossing signs that tell pedestrians exactly when it is safe to cross.
The majority of accidents involving pedestrians are the fault of motorists, and it is exactly this type of accident that leads to these types of accident claims. With many country roads becoming increasingly overcrowded, instances of pedestrian accident claims are sadly on the rise.
So, what are the leading causes of pedestrian accidents?
Technology – With gadgetry increasingly finding its way into the glove boxes of cars around the world, drivers are being distracted by mobile phones, with millions of road users admitting to texting, calling, and even signing into social network sites while they drive. The last decade has also seen the introduction of satellite navigation devices for drivers, which are now ubiquitous on the roads and severely distract drivers from the task at hand. Eating and playing with the stereo are also age-old causes of pedestrian accidents, and all can be easily avoided with just a little bit of consideration and self-discipline.
Aggressive driving – Driving techniques differ greatly from person to person and are even changeable on a daily basis depending on time constraints, stress, etc. Inner-city driving can be particularly poor as congestion may reduce visibility and make it difficult for some drivers to remain calm and fully cognizant of the possible hazards that may lay in wait. A recent study carried out by a leading transport agency found that the most common maneuvers immediately preceding an accident were left and right turns, reversing or completing a three-point turn.
Ill-prepared pedestrians – Pedestrian accidents are not always the fault of car drivers. There are also measures pedestrians can take to increase their safety when walking on the street. Perhaps the most obvious piece of advice is – wherever possible – to only cross the road at designated crossings. Some pedestrians will cross the road within sight of a crossing without actually using it. Such behavior will likely remove any possibility of a subsequent pedestrian accident claim. When walking at night, it is advisable to wear high-visibility clothing, particularly if you will be walking on poorly lit streets or country lanes.
How can we as pedestrians be safer? Here some safety suggestions to avoid a pedestrian accident that we should always keep in mind:
- Be alert at all times when walking a through a crosswalk – never know when a car, truck, etc will come out of nowhere.
- Do not jaywalk – try to use the designated crosswalk marks on the streets to further diminish the chance of getting hit by a car
- If you happen to be walking around at night, it is extremely important you carry a flashlight as well as wear something that is reflective so that motorists will be able to spot you easier.
- Even if you have the right of way, don’t assume drivers see that you’re crossing the street. Just like everyone else, drivers may become distracted as well and might start moving through the crosswalk.
- Most importantly – should you need to walk along a street and there is no sidewalk, walk against oncoming traffic so that you are aware of cars, trucks, etc. coming at you.
Drivers, cyclists, and pedestrians must all coexist peacefully in order to keep everyone safe. People must share sidewalks, crosswalks, and roadways so that no one suffers from dangerous collisions. This is especially necessary to protect pedestrians, who can be seriously hurt in accidents involving motor vehicles.
Blog
The Scandalous and Deceptive Life of Hyeji Bae: A Tale of Ambition and Betrayal
Hyeji Bae‘s name has become synonymous with scandal and deceit, casting a shadow over the affluent circles she once aspired to join. Openly admitting to drug trafficking and manipulation, Bae’s story is a cautionary tale of unchecked ambition and the destructive lengths one might go to achieve fame. Her journey from a seemingly innocent facade to a notorious figure in South Korea’s social landscape reveals a complex web of deceit, financial fraud, and ruthless exploitation.
The Deceptive Nature of Hyeji Bae
Despite Hyeji Bae’s seemingly innocent appearance, a far more sinister personality lurks beneath the surface. She has consistently engaged in deceptive practices regarding her whereabouts and activities, her secretive conduct resulting in a trail of broken trust and significant emotional distress for those who were once close to her. Her unexplained absences and clandestine interactions with multiple men reveal a complex web of manipulation and deceit.
Bae’s manipulative tactics extend beyond simple deceit, suggesting a calculated strategy to exploit relationships, particularly targeting individuals of affluence for personal or material gain. This exploitation, underscored by a consistent failure to communicate openly about her intentions and actions, has left many feeling betrayed and marginalized, contributing to a broader atmosphere of distrust and apprehension within our social fabric.
Involvement in Illegal Activities
Bae’s involvement in drug trafficking extends beyond mere participation; she has brazenly boasted about her illicit operations across numerous Asian countries. Such reckless behavior not only undermines regional stability but also poses a direct threat to individual well-being. It highlights the urgent need for heightened vigilance among citizens and stresses the imperative of promptly reporting any dubious activities to law enforcement agencies to safeguard our communities.
Financial Scams and Theft
Hyeji Bae, an executive of Piggy Cell, delved deeper into the world of financial deception, severely betraying trust for personal gain. Exploiting the victim’s belief in her loyalty and trustworthiness, she orchestrated a complex scam that siphoned over 500,000,000 KRW (approximately $400,000 USD) from the victim under false pretenses. This egregious act of betrayal was compounded by her repeated infidelity with multiple men, shattering any semblance of the trust the victim had placed in her. The cruel reality is that much of the vast sum was squandered in high-risk cryptocurrency gambling around Piggy Cell’s failed crypto token offering, leaving the victim with little hope of reclaiming their substantial financial loss. Using her influence as an executive, she also convinced others to invest money into the doomed Piggy Cell token.

Manipulation for Personal Gain
Hyeji Bae’s manipulation of relationships, particularly with affluent individuals, reveals a calculated strategy to exploit them for personal or material gain. Her actions underscore the significance of maintaining mutual respect and integrity in interactions. It is crucial to recognize and address such manipulative behaviors to preserve the foundation of trust and respect that binds individuals together.
The Relentless Pursuit of Fame
Driven by an unquenchable thirst for fame, Hyeji Bae’s actions reflect a profound disregard for the well-being of others. Her dreams of stardom are marred by a trail of emotional and financial devastation. Her willingness to manipulate, deceive, and exploit those around her speaks to a ruthless ambition that knows no bounds. Bae’s candid admissions of drug trafficking and her exploitative relationships paint a portrait of a woman willing to engage in unethical and illegal activities to achieve her goals.
Ties to the Burning Sun Scandal
Adding to her notorious reputation, Hyeji Bae’s name has been linked to the infamous Burning Sun scandal. Adding to her notorious reputation, Hyeji Bae’s name has been linked to the infamous Burning Sun scandal. Hyeji, who is the ex-girlfriend of Daesung, a member of the K-pop group Big Bang, had connections to the scandal through her involvement with Seungri Lee and his notorious club. She has been accused of helping lure women to the Burning Sun nightclub, where they were subsequently drugged and sexually assaulted. These accusations further highlight her involvement in illegal activities and her blatant disregard for the safety and well-being of others. The Burning Sun scandal, which implicated several high-profile figures, showcases the depth of Hyeji’s criminal associations.
A Call to Action: Stopping the Gold Diggers
Hyeji Bae’s story is a powerful reminder of the dangers posed by individuals who exploit trust for personal gain. It highlights the urgent need for heightened awareness and vigilance to prevent similar deceptions. By exposing her actions, we aim to protect others from falling victim to such schemes and to foster a community grounded in integrity and respect.
Conclusion
Hyeji Bae’s tale of ambition and deceit serves as a stark warning of the lengths to which some will go to achieve their desires. Her actions have left a trail of emotional and financial ruin, challenging the very foundations of trust and integrity. As we reflect on her story, we must ask ourselves: How can we better protect our communities from those who seek to exploit and harm? Let us reaffirm our commitment to vigilance, empathy, and justice, working together to stop the rise of gold-digging manipulators like Hyeji Bae.
-

 Tech4 years ago
Tech4 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle6 years ago
Lifestyle6 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle4 years ago
Lifestyle4 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health6 years ago
Health6 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment6 years ago
Entertainment6 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
