Lifestyle
The Isleworth Mona Lisa And The Monocular Perspective

Leonardo da Vinci’s Isleworth Mona Lisa is one of the most famous paintings in the world. Art historians and other professionals have studied and analyzed it for centuries. There are many theories about why Leonardo painted the Mona Lisa, what he was trying to depict, and how he achieved his desired results. This article will look closely at the Isleworth Mona Lisa and explore the monocular perspective theory.
What Is The Isleworth Mona Lisa?
The Isleworth Mona Lisa is a painting of Lisa Gherardini, the wife of Francesco del Giocondo. It got its name from Isleworth, London, where Hugh Blaker had taken it to his studio after rediscovering it. It is thought to be an inspiration for Leonardo da Vinci’s second Mona Lisa, which hangs in the Louvre Museum in Paris. A private collector currently owns the Isleworth Mona Lisa.
The Glass Wall
When you look at the Mona Lisa in a mirror, you see a completely different image than when you look at it directly. This is because our eyes are set in our skulls about four inches apart. This distance is called the interocular distance. Each eye sees a slightly different image when we look at an object. The brain then combines these two images into one three-dimensional image.
The problem with the Isleworth Mona Lisa is that it is two-dimensional. It was painted on a flat piece of wood, so there is no way for our eyes to see it in three dimensions. When we look at the Isleworth Mona Lisa, our eyes see two different images, but the brain cannot combine them into one three-dimensional image. The result is that we see a flat, two-dimensional image. The Mona Lisa appears to be staring at us from behind a glass wall.
The Monocular Perspective
So how did Leonardo da Vinci paint the Isleworth Mona Lisa? How did he create a three-dimensional image on a two-dimensional surface? The answer lies in the monocular perspective.
The monocular perspective is a way of painting that uses only one eye. When we look at an object with both eyes, each eye sees a slightly different image. But when we look at an object with only one eye, the brain must combine the two images. This is how Leonardo da Vinci was able to paint the Isleworth Mona Lisa.
He used a technique called sfumato, which is a way of blurring the edges of objects. This made it possible for him to create the illusion of depth. The result is a painting that appears to be three-dimensional, even though it is only two-dimensional.
The Mona Lisas are not the only paintings that use the monocular perspective. Many famous paintings, such as The Last Supper and The Virgin of the Rocks, also use this technique.
The Binocular Perspective
The monocular perspective is not the only way to create the illusion of depth. Another way is to use the binocular view. The binocular view is a way of painting that uses both eyes. When we look at an object with both eyes, each eye sees a slightly different image. This allows our brain to combine the two images into one three-dimensional image. The binocular perspective is often used in landscapes and cityscapes. It is also used in some portraits, such as the Mona Lisa.
So why did Leonardo da Vinci use the monocular perspective? One theory is that he was trying to create a more realistic image. The binocular perspective often makes objects appear smaller than they are. This is because our eyes are four inches apart, and the distance between our eyes and the thing we are looking at is added to the object’s size.
For example, if you hold your hand up to your face, it will appear smaller than it is. But if you hold your hand out at arm’s length, it will appear its true size. Leonardo may have been trying to create a more realistic image using the monocular perspective. He wanted the Louvre Mona Lisa and the Isleworth Mona Lisa to appear their actual size, so he used the technique to make them appear larger.
Both the monocular and binocular perspectives were used in the paintings. This would explain why the paintings appear to be three-dimensional. It is also possible that Leonardo da Vinci was using a new technique that had not yet been discovered.
How did Da Vinci Reinvent Perspective?
The word perspective comes from the Latin word perspicere, which means “to see through.” Perspective is a way of drawing that gives objects their correct size, shape, and position. It is based on the idea that our eyes are four inches apart and that we see objects in three dimensions.
Leonardo da Vinci was the first artist to use the monocular perspective. He was also the first artist to use the binocular perspective. He reinvented perspective by using both eyes to create the illusion of depth.
Final Thoughts
The Isleworth Mona Lisa is a fascinating painting. It is one of the first paintings to use the monocular perspective. It is also one of the first paintings to use the binocular perspective. Leonardo da Vinci was a master of perspective, and his invention of the monocular and binocular perspectives changed the course of art history.
Lifestyle
When a Simple Gesture Turns a Difficult Day Around
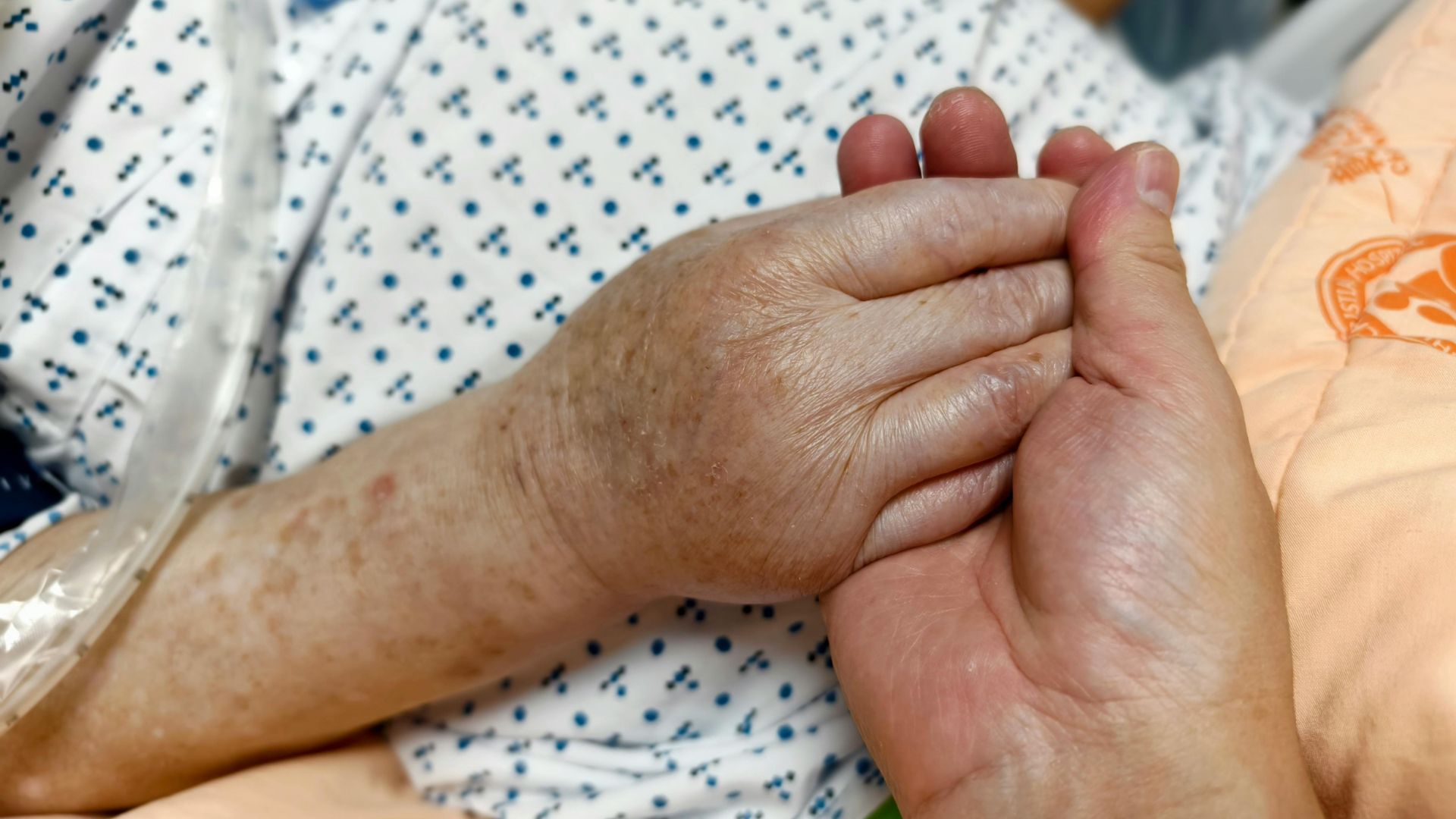
Some days feel hard in ways that are difficult to explain. A person may be dealing with illness, stress, grief, or plain exhaustion, and even the smallest task can feel bigger than usual. From the outside, it may not always be clear what to do. Still, one thoughtful act can shift the mood of the whole day.
That idea is easy to miss in a busy world. People are used to quick texts, rushed check-ins, and good intentions that never quite turn into action. Yet the gestures people remember most are usually simple. A handwritten note. A meal that shows up at the right time. A small gift that says someone thought ahead.
These moments matter because they make a person feel less alone. They do not fix everything, but they change the emotional temperature. They soften the day. They create a pause in the middle of stress, and that pause can mean more than people expect.
Why Small Acts of Kindness Feel So Powerful
When someone is going through a rough patch, support works best when it feels easy to receive. That is part of why a thoughtful get well care package can stand out. It does not ask much from the person receiving it. It simply arrives with comfort, warmth, and a quiet message of care.
That message matters. According to the CDC, social isolation and loneliness are linked to serious physical and mental health risks. Feeling supported is not just emotionally nice; it plays a real role in overall well-being. A caring gesture can remind someone that they are still connected to others, even on a day when life feels narrow and heavy.
There is also something powerful about specific care. A generic “hope you feel better” may be appreciated, but a practical, thoughtful gesture tends to land differently. It shows attention. It tells the recipient that someone slowed down long enough to think about what might actually help.
That could mean comfort food, a cozy blanket, tea, soup, or a short note with the right words at the right time. It could also mean sending something that helps a person rest without making another decision. On difficult days, reducing stress is often just as meaningful as offering encouragement.
The emotional effect of that kind of support can last far beyond the moment itself. People may forget what was said in a hard week, but they usually remember how others made them feel. A kind gesture says, “You do not have to carry this day by yourself.” That feeling can last for a long time.
Thoughtful Support Works Better Than Big Support
One reason small gestures work so well is that they do not need to be dramatic. In fact, the best support is often the least complicated. It does not draw attention to itself. It does not demand a big response. It simply meets a need with care.
That makes a difference in both personal and professional settings. In families and friendships, thoughtful support builds trust. In business, it can strengthen relationships in a way that feels human instead of transactional. Clients, coworkers, and partners notice when kindness feels genuine.
A large gift can sometimes miss the mark if it feels too polished or too distant. A smaller gesture with a personal touch often feels more sincere. Timing matters too. The right support at the right moment will usually mean more than something larger that arrives late or feels generic.
Health experts also note that giving can benefit the person who offers support. Cleveland Clinic cites research showing that helping others can lower stress and support emotional well-being. That helps explain why kind gestures often feel meaningful on both sides. The person receiving care feels seen, and the person giving it gets to turn empathy into action.
There is another reason thoughtful support matters. Many people struggle to ask for help, especially when they are used to being dependable for everyone else. A gesture that arrives without pressure can break through that pattern. It gives the recipient permission to pause, rest, and accept care without having to explain or organize it.
That is often what turns a hard day around. Not a big speech. Not perfect timing. Just one clear sign that somebody noticed.
What People Remember After the Hard Part Passes
Most people do not remember every detail of a difficult season. They remember the moments that made it easier to breathe.
They remember the friend who sent something warm and comforting. They remember the colleague who checked in without making it awkward. They remember the family member who helped practically, rather than saying, “Let me know if you need anything” and leaving it at that.
Those moments stay with people because they feel personal. They show care in a form that can be felt right away. They also create a ripple effect. One act of kindness often inspires another, which is how support grows in families, teams, and communities.
That is what makes simple gestures so valuable. They are not small in impact, only small in scale. On a difficult day, that can be exactly what someone needs most.
The Gesture That Changes More Than a Moment
A hard day does not always call for a grand solution. Sometimes it calls for one thoughtful interruption, something warm, useful, and kind enough to remind a person they are not alone.
That is why small gestures matter so much. They bring comfort without noise. They create connections without pressure. They stay in a person’s memory long after the moment has passed. Whether it is a note, a meal, or a carefully chosen get well care package, the right gesture can do more than brighten a day. It can help someone feel cared for when they need it most.
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle7 years ago
Lifestyle7 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle6 years ago
Lifestyle6 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health7 years ago
Health7 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment7 years ago
Entertainment7 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
