Business
Know What Makes A Matboard Supplier for IKEA China Professional

IKEA is a Swedish furniture store. It is a multinational retailer of household goods. IKEA has branches in many countries around the world, selling flat-packed furniture, accessories, bathrooms and kitchen supplies as a pioneer in the sale of self-assembled furniture at reasonable prices and is currently the world’s largest furniture retailer.
Therefore, if other companies that want to cooperate with large-scale companies like IKEA must meet relatively high standards. As for matboards, what makes a matboard supplier for IKEA China professional?
As the biggest matboard manufacturer basement in China, DY Matboard has relatively good quality which can compare to US and Italian matboard. This stable quality requirement make us the unique matboard supplier to IKEA in China. The reasons why DY did it are as followed.
1. Supreme & environmentally-responsible raw materials
IKEA is always associated with improving people’s quality of life and adhering to the business tenet of “provide as many customers as possible, well-designed, well-functioning, low-cost household items”. While providing a wide variety of beautiful and practical household items that ordinary people can afford, IKEA strives to create a business model centered on customers and the interests of society, and is committed to environmental protection and social responsibility issues. The IKEA way of purchasing home furnishing products: IKEA’s policies on environmental protection and forest resources are very strict.
As a manufacturer that values environmental protection, DY uses acid-free paper and has passed FSC certificate successfully. The FSC is made up of representatives from environmental protection organizations, government forestry departments, local resident organizations, social forestry groups and timber product certification bodies from more than 70 countries. Its international center was originally located in the capital of Oaxaca, Mexico. FSC is a relatively mature and complete forest certification system.
DY insists on using acid-free paper. The PH of mat boards is 7.0 (neutral) or higher (alkaline) means they’re acid-free. Under normal conditions of use and storage, the life of acid-free paper can reach 200 years. Permanent paper can last for at least centuries without significant deterioration. The paper generally has a pH of 7.5 or higher and does not contain groundwood pulp, so it has high strength and high paper properties, and is suitable for people to use and store for a long time.The basis weight and color of the paper depend on the application. The paper is solid, strong and close to neutral. After special treatment (eliminating the organic acid present therein) from the plant fiber pulp, it is made on a paper machine.
2. World-class equipment & experienced technicians
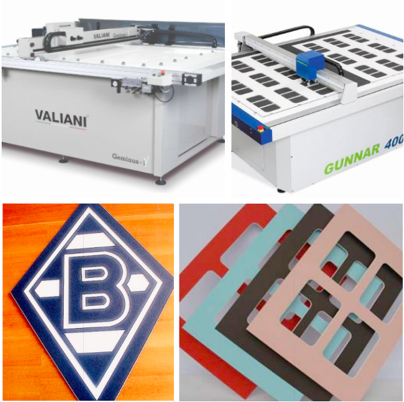
DY also bring in the cutting machines from Italy (Valiani) and Netherland (Gunnar). For over several years, Valiani and Gunnar products have consistently reset the bar of excellence for precision cutting in the matboard and framing industries. DY has more than 20 Valiani and Gunnar cutting machines , Now we cut 150000 mat board sheets each day , have the largest production capacity in China.
The company has more than ten years of professional and technical personnel with strict production management team. The fully automatic computer cutting unit can perform pipeline management and control operations, and can produce 45 degree opening (forward and reverse bevel effect), single layer, double-layer, porous, and shaped mat boards can also be customized according to customer requirements.
3. Diverse applications
The mat boards can be used as delicate picture frames and decoration with diverse cuttings. DY offers uncut, precut and custom mat board at wholesale prices. A matboard manufacturer that often innovate and develop new products to meet the changing needs of the customers and looking for ways to elevate the industry, products and processes.

For example, black mat board features: fine paper, smooth surface and is robust. Applicable to clothing bags, gift boxes, clothing tags, shoe boxes and other packaging.
The New York brand Lafayette 148 clothing tote bag is made of black mat board, the paper bag is covered with embossing, which increases the three-dimensional and artistic atmosphere of the paper bag. The logo is white gold, with fine workmanship. The black bag is in line with the simple atmosphere of Europe and America.
Black cardboard is not suitable for color printing because it is black on both sides, usually using hot stamping. This Saatchi box body is only made of hot stamping in the LOGO. It is very simple, but it is also matched with black. It is very conspicuous. The carton is covered and embossed to give the entire carton a more fashionable feel.
The black color of black cardboard is a very solemn color, but it can make other colors stand out. We can often see the combination of black and bright colors, black cardboard is used in the packaging of business gift boxes because of its elegant color. DY offers mat boards with different colors and textures.
To be a professional mat board supplier off IKEA, the company must adhere to high standard and continues to develop itself. DY aims high and is ready to provide high-quality mat boards.
Business
Remote Professionals Getting More Value for Their Work Thanks to Borderless Banking

Not too long ago, the idea of working remotely from an island in Thailand or a co-working space in Berlin sounded like the kind of fantasy only tech moguls or backpacking freelancers could afford.
Fast forward to today, and it’s as good as a global reality. Millions of professionals have cut the cord from traditional office life in exchange for flexibility, freedom, and a work-life balance that fits their personal rhythm and not their employer’s timezone.
However, as remote work has reshaped how people earn a living, it’s also pointed out the existing limits to most of the world’s financial systems. Traditional banking simply wasn’t built for a workforce that’s always on the move, operating in multiple currencies, and getting paid across borders.
Thankfully, that’s where borderless banking like Black Banx have proven vital, and has quietly transformed the way money is managed for people vacationing and working overseas alike.
The Rise of the Remote Work Economy
Remote work isn’t just a pandemic-era trend that faded with Zoom fatigue—it’s become a defining feature of the modern workforce. A recent survey revealed that over 39% of Gen Z and Millennials planned to live and work abroad for extended periods this year, many staying six months or more in a single location. That’s beyond a short trip, and can be considered as good as a sabbatical with a substantial lifestyle shift.
According to recent estimates, the digital nomad economy now also contributes as much as US$787 billion annually to the global economy. And this isn’t just entry-level gig work. A third of digital nomads earn between US$100,000 and US$250,000, while another third take in US$50,000 to US$100,000 annually.
It is indeed evident that the manner in which many make a living has changed. Unfortunately, most financial systems haven’t kept up.
Where Traditional Banks Are Still Falling Short
For those who have ever tried to open a bank account abroad or receive payment from a foreign client, they already know the drill: the paperwork is endless, delays are frustrating, and the fees? So much to do, even for the smallest amounts of money.
Just to name few of the hurdles remote workers still face with conventional banking:
- Account setup restrictions: Need proof of residence, tax IDs, or a local job offer—things many digital nomads simply don’t have.
- Slow international transfers: Payments can take days to process, which is a nightmare when rent’s due.
- High foreign exchange fees: Currency conversions often come with steep, hidden costs.
- Limited multi-currency support: Most banks still force users to operate in a single currency, making financial planning chaotic at best.
And perhaps most tellingly, many banks have digitized their operations but haven’t personalized their services. According to Accenture’s 2025 Banking Trends Report, while digital transformation has improved efficiency, it often sacrifices the customer experience. That’s not great news for people who live outside the lines.
Borderless Banking for Professionals Across the Globe
The concept of borderless banking goes far beyond wiring money internationally. Fundamentally, it’s also about being able to eliminate the friction between people and their money, no matter where they are in the world, and maintaining an ecosystem where geography, bureaucracy, and currency don’t stand in the way of financial freedom.
A working example of this is Black Banx, a Toronto-based fintech founded by German billionaire Michael Gastauer. Since launching globally in 2015, it has grown to serve over 78 million clients in 180+ countries as of Q1 2025, proof that people take to digital banking solutions when it is accessible, affordable, and is useful in just about any locale.
In the first three months of this year, Black Banx had also earned US$4.3 billion in revenue and US$1.6 billion in pre-tax profit, more than double from the same quarter the previous year and showing it has consistently delivered tangible value to global customers—remote professionals included
How Borderless Banking Maximizes Value for Remote Workers
1. Instant Account Access—No Strings Attached
The times of hunting down local branches or collecting endless documents just to open an account are finished. With borderless banks, users can open an account in minutes using just a photo ID—no proof of address or income required. That’s a lifesaver for anyone living outside their passport country or hopping from one location to another.
2. Multi-Currency Mastery
Managing money in multiple currencies used to mean juggling several accounts—or worse, losing money on conversions. Borderless platforms like Black Banx support 28 FIAT currencies and allow real-time currency conversions at competitive rates. That means remote workers can:
- Invoice clients in one currency
- Spend or save in another
- Hedge against local currency fluctuations
- Avoid excessive conversion fees altogether
3. Seamless, Real-Time Global Payments
Getting paid late, or paying others late, isn’t just inconvenient; it can damage relationships and disrupt your cash flow. With real-time payment support, remote workers can receive funds instantly, no matter where their clients are. This is particularly valuable for freelancers and entrepreneurs juggling multiple contracts across time zones.
Plus, bulk payment features and API integration streamline processes for those running teams or businesses.
4. Built-In Crypto Options
It isn’t surprising that many digital nomads are already deep into crypto. Whether it’s for investment, faster transactions, or avoiding traditional finance red tape, crypto is becoming essential.
Since 2016, Black Banx has allowed users to send, receive, and convert crypto (like BTC and ETH) within their accounts. That integration saves users from having to manage separate crypto wallets, and adds another layer of flexibility to their financial toolkit.
5. Secure Transactions
Remote workers often log in to work from cafés, coworking spaces, and airports, to name a few. Of course, this flexibility of being able to work almost anywhere should never come at the cost of security. Borderless banks like Black Banx use end-to-end encryption, AI fraud detection, and two-factor authentication to keep accounts safe from risky elements.
Financial Freedom, Not Just Convenience
Perhaps the most overlooked benefit of borderless banking is the freedom it provides. Not just to access money, but to fully participate in the global economy. For millions of professionals in underbanked regions like Africa, Latin America, Southeast Asia, borderless banking has become a gateway to financial inclusion and a way to take on opportunities that typically wouldn’t be available to them if not remote.
By removing barriers to entry, platforms like Black Banx empower underserved individuals to both take control of their finances and increase their earning power by working with companies from higher paying markets. This democratization of finance isn’t just good for individuals, it’s good for the global economy as a whole.
As Black Banx CEO Michael Gastauer put it: “Our multi-currency solutions enable businesses to tap into global talent without worrying about payment complexities. We make cross-border transactions as seamless as local ones.”
The Road Ahead
By 2030, the number of digital nomads worldwide is expected to soar past 60 million, according to the Forbes Technology Council. That means tens of millions of workers will be navigating foreign currencies, time zones, and financial systems—all while expecting the same seamless experience they’d get at home.
Indeed, remote professionals aren’t just looking for places to work—they’re looking for systems that work for them. In a lifestyle built on flexibility, traditional banking is proving too rigid, too slow, and too expensive.
Borderless banking services like those offered by the likes of Black Banx, on the other hand, offer exactly what today’s global workforce needs: instant access, multi-currency support, real-time payments, crypto integration, and enterprise-level security—all in a streamlined experience.
-

 Tech4 years ago
Tech4 years agoEffuel Reviews (2021) – Effuel ECO OBD2 Saves Fuel, and Reduce Gas Cost? Effuel Customer Reviews
-

 Tech6 years ago
Tech6 years agoBosch Power Tools India Launches ‘Cordless Matlab Bosch’ Campaign to Demonstrate the Power of Cordless
-

 Lifestyle6 years ago
Lifestyle6 years agoCatholic Cases App brings Church’s Moral Teachings to Androids and iPhones
-

 Lifestyle4 years ago
Lifestyle4 years agoEast Side Hype x Billionaire Boys Club. Hottest New Streetwear Releases in Utah.
-

 Tech7 years ago
Tech7 years agoCloud Buyers & Investors to Profit in the Future
-

 Lifestyle5 years ago
Lifestyle5 years agoThe Midas of Cosmetic Dermatology: Dr. Simon Ourian
-

 Health6 years ago
Health6 years agoCBDistillery Review: Is it a scam?
-

 Entertainment6 years ago
Entertainment6 years agoAvengers Endgame now Available on 123Movies for Download & Streaming for Free
